Architectural Design
This section provides a detailed overview of Beyond's system architecture, focusing on the core components and their interactions. Additionally, you will find other sources of information in:
- The Security Measures section (see also the Audit and Bug Bounty links).
- The Beyond SDK specification, which you can use to quickly make your dApp interoperable with the entire Bitcoin ecosystem (note: for Beyond to list your chain or token, please contact the team instead).
- The Beyond Monorepo, a single repository to explore the entire codebase on GitHub.
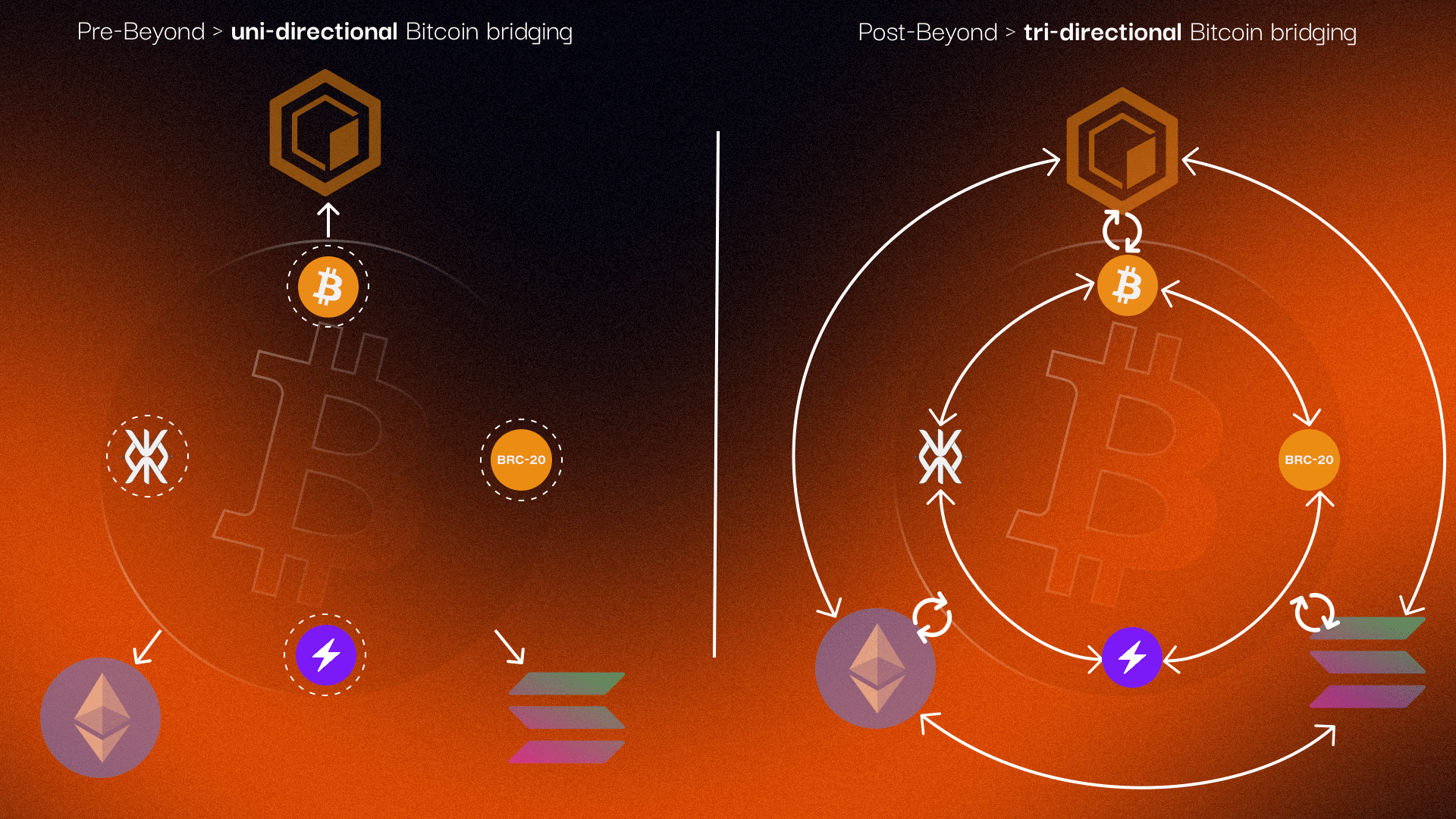
Core Components
In simple terms, the asset bridging process involves locking native tokens on the source chain, and minting wrapped tokens on the destination chain. This process is facilitated by a combination of on-chain and off-chain components that ensure seamless interoperability and asset transfer across different blockchain ecosystems.
NodesandIndexers: Together they facilitate transactions and indexing on all blockchains, ensuring real-time data accuracy and accessibility. These components are sometimes called RPC nodes and Subgraph indexers.Registry: A database consolidating data from various sources (e.g. indexers) into a unified repository with extended business logic.CoreandRelayerContracts: A set of smart contracts that mint and burn tokens on non-Bitcoin-L1 chains.Forge: A validator-controlled entity (multi-party computation) that locks and unlocks tokens on the Bitcoin L1.
Initially, the Forge is secured by 11 signers, with a 7-key threshold needed to authorize transactions. This approach mirrors the battle-tested system from industry leaders like LayerZero or Wormhole, ensuring a high degree of security. For Beyond V1, the Forge is permissioned, while V2 becomes permissionless via staking.
User Journey Examples
Avalanche ➤ Bitcoin
- User locks AVAX tokens in Beyond's
Relayersmart contract on Avalanche, which also triggers a cross-chain event via LayerZero messenger for theCorecontract on Bitcoin. - Beyond's
Forgelistens to the cross-chain event, sends wAVAX wrapped tokens to the user's wallet on Bitcoin, then waitsnblocks for immutable confirmation. - Bitcoin indexer and
Registryupdate with the mint event.
Bitcoin ➤ Avalanche
- User burns wAVAX wrapped tokens via Bitcoin
Forge. - After
nblocks, Bitcoin network immutably confirms the transaction, Bitcoin indexer andRegistryupdate with the burn event, while a cross-chain event is triggered via LayerZero messenger. - The original AVAX becomes unlocked in Beyond's
Relayersmart contract on Avalanche, and sent to the user's wallet.
Bitcoin (BRC-20) ➤ Bitcoin (Runes)
- User locks native ORDI (BRC-20) tokens in the Bitcoin
Forge. - After
nblocks, Bitcoin network immutably confirms the transaction, Bitcoin indexer andRegistryupdate with the lock event, while a Bitcoin event is triggered. - Beyond's
Forgemints wORDI (Runes) and sends it to the user's wallet. - If the same or another user wants to switch back to BRC-20, the process is identical in reverse order: burn wORDI (Runes) and retrieve the original ORDI (BRC-20).